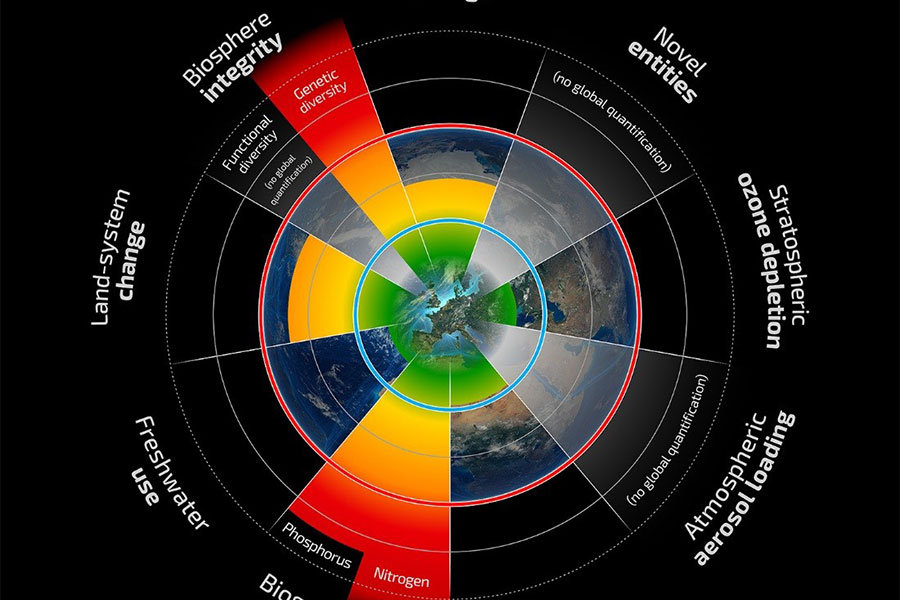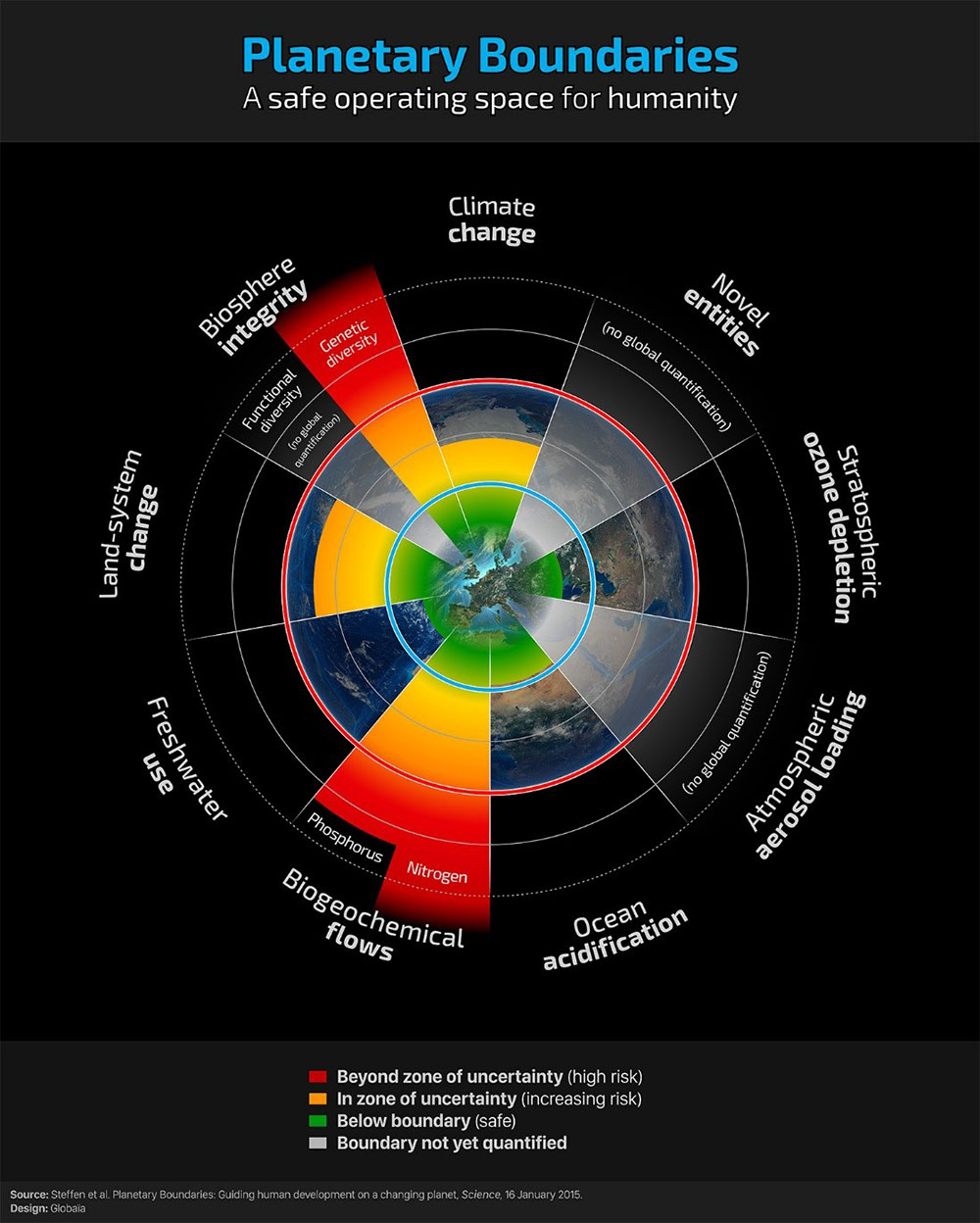
The 9 planetary boundaries define the health condition of our Planet Earth. CO2 with Global Warming and Climate Change (GWCC) is only 1 of 9 Planetary Boundaries.
CO2 in the atmosphere from burning fossil fuel (oil, diesel, petrol, coal and more) is creating a greenhouse effect resulting in the temperature raising. The way to measure CO2 in the atmosphere is parts per million- ppm.
CO2 in the atmosphere was 280ppm before the industrial revolution. The maximum healthy value for CO2 is 350 (some scientists calls it “tipping point”).
CO2 is now (in 2018) 400 ppm. Having crossed the maximum healthy point, we start feeling the warming of the earth. The hottest temperature ever measured was in 2018. Global Warming and Climate Change has started and is here now.
Most people know about CO2 and GWCC. Fewer people know about all the 9 boundaries.
The nine planetary boundaries give a more precise picture of how our Planet is doing and the stress human activities are causing.
The planet is like a living organism. It can regulate and repair itself, but there are limits, and those can be exceeded and lead to big catastrophes or death and extinction. That is why scientists have started to define the 9 most critical limits or boundaries, which should not be exceeded.
Why?
The current worldwide economic system is allowing industrial companies to grab the planets resources for free and on the way pollute the soil, air and water, then make people consume as much as possible and create a lot of waste. The industrial companies and corporations are very seldom bothered by or held responsible for the mess and the waste following their activities. Governments, non-profit organizations, community groups and activists are those to eventually discover the mess and do something about it.
Here are some details about the 9 planetary boundaries:
Scientists around the world agree on these 9 main Planetary Boundaries for our Planet Earth:
- CO2 in the atmosphere with Global Warming and Climate Change (GWCC)
- Biodiversity loss
- Nitrogen cycle disturbance, Phosphorus
- Ocean acidification
- Land use
- Fresh water resources
- Ozone depletion
- Atmospheric aerosols
- Chemical pollution
These 9 Boundaries were proposed to the scientific world by Swedish scientists in 2009, and not all of them are clearly defined yet.
Fore details about planetary boundaries go to:
http://www.stockholmresilience.org/research/planetary-boundaries.htmlen%20identified
The scientists work with 3 values for each boundary:
- a value from before industrialization began (1945),
- a tipping point, which they estimate cannot be exceeded without significant changes on earth, and
- the present state for nine Earth systems:
Climate Change – CO2 concentration in the atmosphere is what most people are focusing on when describing the danger for our planet for not being able to reverse the consequences of the greenhouse effect and global warming. As mentioned before, the boundary has already been crossed and has reach 400 ppm.
Biodiversity loss – loss of species and family of species has already crossed the boundary. It is measured in extinction rate of species – number of species per million per year. The boundary is 10 and the current value is more than 100. If it continues with current speed 1/3 of all species will
Nitrogen cycle disturbance and Phosphorus – Nitrogen has a cycle where nitrogen from the atmosphere is converted into a new inactive form in the soil and it is polluting waterways and coastal areas. Only a small part of the fertilizer in agriculture is used by plants. Most nitrogen and phosphorus end up in rivers. This form of phosphorus cannot be reuse and the reserves are running out in the next 50-100 years. The boundary for nitrogen in the atmosphere has already been crossed. Phosphorus is measured by millions of tons going into the ocean. Pre-industrial there was nothing. The tipping point is 11 and it is now 9.
Ocean acidification– meaning the surface acidity of the ocean. It has increased 30 % since the industrial revolution. This boundary is totally connected to climate change and CO2 generated by use of fossil fuel. Excess CO2 is dissolved in the ocean. Pre industrial value is 3.44 and it is currently 2.90
Land use is the surface of land used for agriculture in percent. The measure for pre industrial time was just low. The tipping point is 15% and it is now 11.7%
Fresh water resources. Chemicals and pollution are having a dramatic effect on fresh water systems. It is measured in human consumption. Pre industrial value was 415 km2/year and it is now 2600 km2/year.
Ozone depletion – The ozone layer is a part of the Earth’s stratosphere. It absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the sun. In 1970ties scientist discovered holes in the ozone layers near the poles but also at times in other areas of the planet. The cause was use of certain gasses used in spray bottles and refrigerators. Many countries banned these gasses in 1989, because holes in the ozone layer is a big problem for humans. It causes skin cancer, cataracts, genetic and immune system damage. The ozone layer started to recover in 2000 (after laws (from 1989) banning the use of CFC (freon) in the production of fridges and in freon sprays) and is improving little by little. This is an example of how it helps the planet and humans to ban a dangerous substance. It is measured as the concentration in the stratosphere. Pre-industrial value was 290. Current value is 283.
Atmospheric aerosols – These are particles in the atmosphere. There natural aerosols like monsoons and volcanos, but with all the industrial production has followed a lot more particles in the air from fossil fuel and many chemicals. This goes up in the atmosphere. It can have the same effect as CO2 – preventing the heat from the sun to reflect back and in this way contribute to a warmer planet. The values for this have not yet been identified
Chemical pollution – land, water and air are already dangerously polluted. The scientists are still working to evaluate many of the values. Land is polluted by waste from the landfills, water is polluted by hundreds of thousands of chemicals and fertilizers from factories and agriculture plus single-use-plastic being dumped in the ocean every minute. Air is polluted by incineration of waste and by burning of fossil fuels. Many of the chemicals in all types of pollution are very dangerous to animal and human health. In addition, there is noise and light pollution also contributing to serious health problems.
Read more about chemical pollution on this website:
https://www.livescience.com/22728-pollution-facts.html